If you’ve just run a speed test and are staring at the numbers on your screen wondering what they actually mean for your daily browsing, you aren’t alone. We understand that seeing a number that doesn’t match your expectations—or your monthly bill—can be frustrating.
Internet speed test results can be confusing because they represent a snapshot of your connection’s maximum capacity at a specific moment, not necessarily the consistent speed you experience while watching Netflix or hopping on a Zoom call. To truly understand your internet performance, you need to look beyond the raw numbers and understand the relationship between bandwidth, speed, and congestion.
What Is Internet Bandwidth?
When we talk about internet bandwidth, we are referring to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over your network connection in a given amount of time. It is essentially the capacity of your connection.
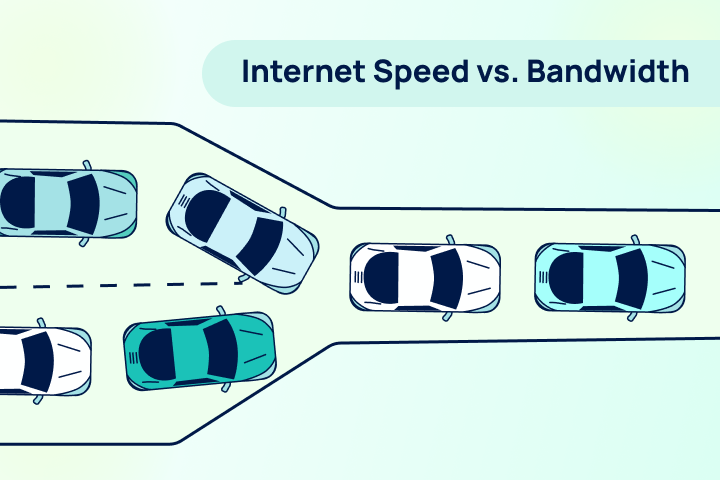
Think of bandwidth like a highway. The bandwidth is the number of lanes on that highway. A wider highway (higher bandwidth) allows more cars (data) to travel side-by-side simultaneously. This capacity is crucial for modern households where remote work, streaming 4K video, and online gaming happen all at once.
If you have a narrow highway (low bandwidth) and try to push too much traffic through it, everything slows down. That’s why having sufficient bandwidth is critical for Zoom meetings and ensuring your video streaming doesn’t buffer constantly.
Bandwidth vs. Internet Speed: What’s the Difference?
While they are often used interchangeably, the concepts of internet bandwidth vs speed are distinct.
- Bandwidth answers the question “How much?” It is the total capacity of the pipe.
- Speed answers the question “How fast?” It is the rate at which data moves through that pipe.
To go back to our highway analogy: Bandwidth is the number of lanes, while internet speed is the speed limit (or how fast the cars are actually driving).
It is important to understand the difference between download vs. upload speeds within this context. Most residential internet connection types—like cable or DSL—offer asymmetrical bandwidth, meaning you have a wide highway for downloading data but a narrow lane for uploading it. Gigabit internet via fiber, however, often provides symmetrical bandwidth, giving you maximum capacity in both directions.
How to Understand Your Internet Speed Test Results
When you look at your results on TestMySpeed, you are seeing a real-time measurement of how your bandwidth and speed are performing together. Understanding internet speed metrics is the first step toward fixing a slow connection.
Here is a breakdown of what you are looking at:
- Download Speed: How quickly your network can pull data from a server (loading a webpage, streaming a video).
- Upload Speed: How quickly you can send data (posting to social media, your video feed on a conference call).
- Latency (Ping): It’s the time it takes for a signal to travel from your device to the server and back. High latency causes lag, even if your speed numbers look high.
If your results are lower than expected, check if your ISP is throttling your internet or if you aren’t getting the speed you’re paying for.
Internet Speed Result Tiers: What Different Speeds Mean
Not sure if your result is “good”? Here is a quick guide to what different speed tiers typically handle.
Find how much Internet Speed do you need
Your household may want faster internet speeds.
<50 Mbps
Great for individuals to browse the internet, check email, and other basic browsing.
50-100 Mbps
Great for streaming Netflix, videos, and online meetings.
100-200 Mbps
Great for streaming high quality videos, fast downloads, video games, and multiple devices.
200+ Mbps
Great for doing almost anything at ultra fast speeds.
How Bandwidth Affects Real-World Internet Speed
It is vital to remember that the bandwidth vs speed dynamic is affected by your environment. Bandwidth is a maximum limit, not a guarantee.
Several factors can reduce your actual speeds below your bandwidth cap:
- Network Congestion: Just like rush hour traffic, internet traffic affects speed. If everyone in your neighborhood is online at 7 PM, your cable connection might slow down.
- Weather: Does weather affect internet speed? Yes, extreme conditions can impact performance. Especially for satellite and fixed wireless connections.
- Hardware: An old router or modem acts like a bottleneck, limiting the bandwidth that actually reaches your device.
- Connection Type: As explained in our guide to internet connection types, fiber is generally more consistent than DSL or satellite.
How Multiple Devices & Concurrent Connections Impact Speed
The most common reason for “slow” internet isn’t always the provider—it’s the number of concurrent connections.
Every device connected to your Wi-Fi takes up a lane on that bandwidth highway. If you are working remotely while the kids are gaming and the TV is streaming 4K, you are splitting your total bandwidth three ways.
This division often results in high latency and buffering, because your capacity is maxed out. Even a fast connection can crawl if it’s overloaded. Understanding streaming data usage can help you manage these bottlenecks better.
Managing Bandwidth for Better Performance
If your internet speed test results are consistently low, optimization might help before you commit to paying for a pricier plan.
- Prioritize Traffic: Many modern routers allow you to prioritize bandwidth for specific devices (like your work laptop) using Quality of Service (QoS) settings.
- Check for Throttling: Sometimes the issue is on the provider side. Learn how to tell if your ISP is throttling your connection.
- Upgrade Hardware: Ensure your router can handle the gigabit speeds if you are paying for them.
- Identify Slowdowns: Read up on the 15 reasons for slow internet to troubleshoot hidden issues like interference or background updates.
FAQs: Understanding Internet Speed Test
FAQs: Understanding Internet Speed Test
Why is my speed test slower than my internet plan?
Speed tests measure real-time performance, which is affected by Wi-Fi interference, network congestion, and the capabilities of the device you are testing on. Wired connections usually yield results closer to your plan’s advertised speed.
Is bandwidth the same as internet speed?
No. Bandwidth is the total capacity (how much data can be moved), while speed is the rate of transfer (how fast the data moves). You need both for a smooth online experience.
How many Mbps do I really need?
For basic browsing, 25 Mbps is sufficient. For 4K streaming and remote work, aim for at least 100 Mbps. Households with 4+ heavy users should look for 200 Mbps or higher.
Why does my internet slow down at certain times of day?
This is likely due to network congestion, often called “peak hours” (usually evenings), when many people in your neighborhood are online simultaneously.
Speed Test Are Only the Beginning
Your TestMySpeed results are a diagnostic tool—a way to peek under the hood of your connection. By understanding the balance between internet bandwidth and speed, you can decide whether you simply need to kick a few devices off the Wi-Fi or if it’s time to call your provider for an upgrade.
Recommended Reading: